Looking for Summary and Comparison of Home Food Preservation Methods in 2026? Scroll down this page and follow the links. And if you bring home some fruit or vegetables and want to can, freeze, make jam, salsa or pickles, see this page for simple, reliable, illustrated canning, freezing or preserving directions. There are plenty of other related resources, click on the resources dropdown above. If you are having a hard time finding canning lids, I've used these, and they're a great price & ship in 2 days.
If you have questions or feedback, please let me know! There are affiliate links on this page. Read our disclosure policy to learn more.
Summary and Comparison of Home Food Preservation Methods:
Canning (bottling), freezing, drying, pickling, jam/jelly making and fermenting
Below are general descriptions of common, safe home food preservation methods. Click on the links to see tested recipes and directions using these methods. Also see this page for a glossary of terms used in home preserving.
Approved Safe Home Preservation Methods
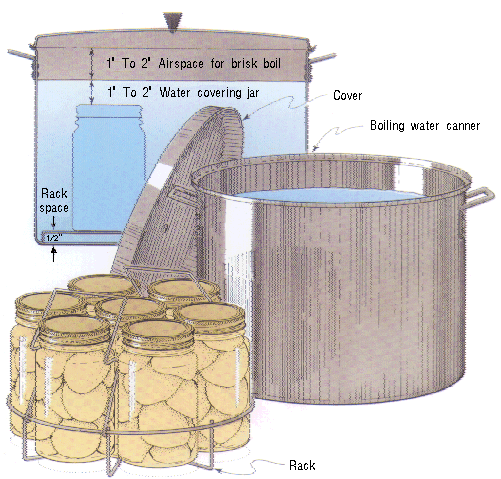
- Canning is the process in which foods are placed in jars or cans and heated to a temperature that destroys microorganisms and inactivates enzymes. This heating and later cooling forms a vacuum seal. The vacuum seal prevents other microorganisms from decontaminating the food within the jar or can. Acid foods such as fruits and tomatoes can be processed or "canned" in boiling water (also called the "water bath method"), while low acid vegetables and meats must be processed in a Pressure Canner at 240°F (10 pounds pressure at sea level). See this page for why you should use a canner and how to choose one. There are a large number of unsafe canning methods that people use, from the no processing at all (just fill the jars and seal, called "open kettle" canning) to oven canning, microwave canning and even using the dishwasher. See this page for a description of these unsafe methods, why they are dangerous and links to references about them.
- Pickling is another form of canning. Pickled products have an increased acidity that makes it difficult for most bacteria to grow. The amount of acid present is very important to the safety of the product. Pickled products are also heated in jars at boiling temperatures to destroy any other microorganisms present and form a vacuum in the jar.
- Jams and Jellies have a very high sugar content. The sugar binds with the liquid present making it difficult for microorganisms to grow. To prevent surface contamination after the product is made and thus possible yeast or mold growth, these are either canned, frozen, or refrigerated.
- Freezing reduces the temperature of the food so that microorganisms cannot grow, however many will survive. Enzyme activity is slowed down, but not stopped during freezing.
- Drying removes most of the moisture from foods. Thus microorganisms cannot grow and enzyme action is slowed down. Dried foods should be stored in airtight containers to prevent moisture from rehydrating the products and allowing microbial growth.
(Source: So Easy To Preserve, 4th edition, Cooperative Extension Service, The University of Georgia)
Water Bath Canner
|
Pressure Canner
|
Are you following the latest canning recommendations?
Canning guidelines were revised in 1989 following extensive research. Canning instructions printed before 1989 may be unsafe. Here are some of the newer recommendations you should be using (these are incorporated into all of the recipes on pickyourown.org - we use only the most up-to-date directions and recommendations from the USDA, Ball and major university food science labs:
- Bottled lemon juice should be added to all canned tomatoes.
- Jellies, jams, and preserves should be processed in a boiling water bath.
- Pickles and pickled products should be processed in a boiling water bath.
- The pressure for your pressure canner and the time for processing in a boiling water bath should be adjusted according to your local altitude.
Looking for canning equipment and supplies?
Water bath canner with a jar rack
Pressure canners for gas, electric and induction stoves: Presto 23Qt or T-fal 22Qt
Canning scoop (this one is PERFECT)
Ball Blue book (most recent version)
Jars: 8oz canning jars for jams
Want to start your own Podcast, Blog, Vlog, etc? This GoPro kit has EVERYTHING you need: GoPro Hero Black Compact - Waterproof Action Camera with 4K Ultra HD Video and all accessories
Find Other types of farms:
Farm markets and roadside stands
Road trips and camping resources
Local Honey, apiaries, beekeepers
Consumer fraud and scams information
Home canning supplies at the best prices on the internet!
Maple Syrup Farms, sugarworks, maple syrup festivals
Environmental information and resources
Farms For Your Event for birthday parties, weddings, receptions, business meetings, retreats, etc.
Festivals - local fruit and vegetable festivals
Get the
most recent version of
the Ball Blue Book
With this Presto 23 quart pressure canner and pressure cooker, you can "can" everything, fruits, vegetables, jams, jellies, salsa, applesauce, pickles, even meats, soups, stews. Model 01781

You can make jams, jellies, can fruit, applesauce, salsa and pickles with water bath canners, like this Granite Ware 12-Piece Canner Kit, Jar Rack, Blancher, Colander and 5 piece Canning Tool Set